- Phone: +86 132 8320 1810
- Email: annie@wrkgroup.ltd
-
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
ሐምሌ . 08, 2025 06:16 Back To List
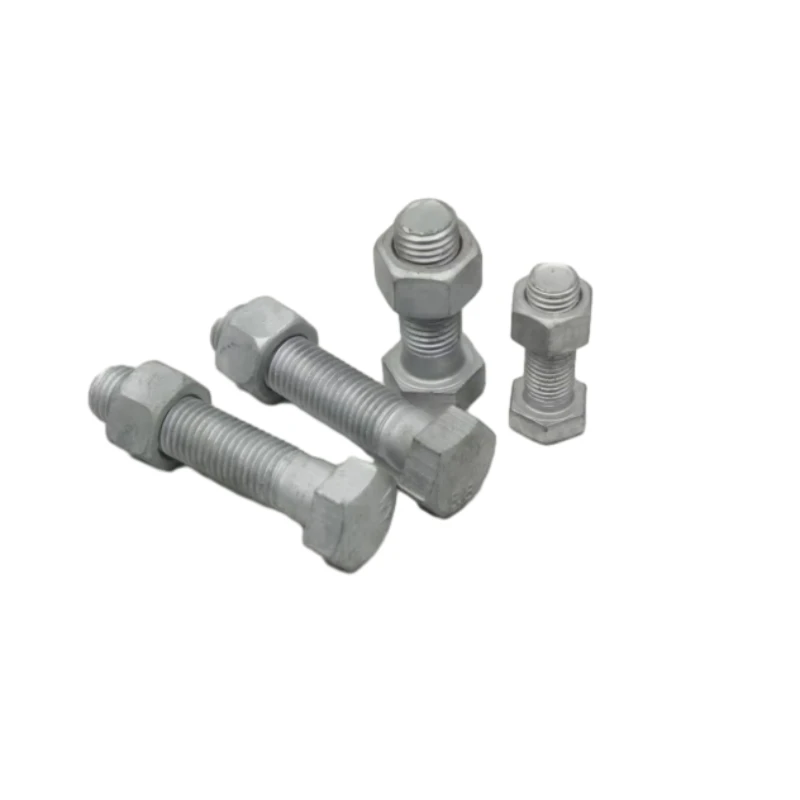
Tiny Nuts and Bolts for Precision Projects Complete Nuts, Bolts, and Washers Sets
- Introduction: Understanding Tiny Nuts and Bolts
- Technical Specifications and Material Advantages
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Suppliers
- Customization Options and Emerging Trends
- Applications Across Precision Industries
- Case Studies: Innovations in Use
- Conclusion: The Essential Role of Tiny Nuts and Bolts

(tiny nuts and bolts)
Introduction: Understanding Tiny Nuts and Bolts in Modern Engineering
In the realm of precision components, tiny nuts and bolts
have evolved into vital elements that enable technologies across microelectronics, medical devices, automotive sectors, and aerospace engineering. As industries trend towards compact designs, the relevance of these miniature fasteners continues to surge. According to recent market analytics, the global micro fasteners market is projected to reach $1.7 billion by 2027 with a CAGR of 7.8% from 2022. These figures are driven by escalating demand for lightweight, high-strength assemblies that maintain durability despite size constraints. Tiny nuts and bolts, though generally less than 2 millimeters in diameter, must nevertheless surpass stringent standards for tensile strength, torque, and corrosion resistance. Their significance cannot be overstated; a single defective fastener can compromise an entire assembly, highlighting the precision engineering needed in their manufacture.
Technical Specifications and Material Advantages
The technical characteristics of micro fasteners such as nuts and bolts and screws are defined by their size, material composition, threading, and surface treatments. Standard material choices include stainless steel (300 and 400 series), titanium, brass, and high-grade alloys, each offering unique benefits. For instance, stainless steel micro fasteners provide robust corrosion resistance and elasticity, making them especially suitable for medical and marine applications. Brass is favored for electronic assemblies due to its magnetic neutrality. A standard grade A2-70 stainless steel M1.6 bolt demonstrates a tensile strength of up to 700 MPa, matching or exceeding larger counterparts. Additional surface treatments, such as passivation or black oxide coating, are implemented to bolster corrosion resistance and reduce friction during installation. Assembling nuts and bolts and washers in critical environments requires attention to thread tolerance and stress relaxation, a demanding process that underscores the sophistication behind each component.
Comparative Analysis of Leading Suppliers
Selecting the right supplier is fundamental to ensuring performance, consistency, and cost-effectiveness in tiny fastener procurement. The table below compares three industry-leading vendors based on parameters such as minimum size capability, material diversity, QC certifications, lead time, and average batch rejection rates:
| Supplier | Minimum Size (mm) | Material Options | Certifications | Lead Time (days) | Batch Rejection Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Micro Fasteners Inc. | 1.0 | Stainless Steel, Brass, Titanium | ISO 9001, AS9100 | 12-18 | 0.13 |
| MicroThread Solutions | 0.8 | Steel, Alloy, Copper | ISO 14001, IATF 16949 | 14-20 | 0.21 |
| NanoBolt Tech | 0.5 | Stainless Steel, Titanium | ISO 9001, RoHS | 9-15 | 0.09 |
Among these, NanoBolt Tech stands out for its ability to produce bolts as tiny as 0.5 mm with the lowest rejection rates, resulting in lower wastage and higher assembly reliability. Certifications such as AS9100 and IATF 16949 indicate strong quality management within aerospace and automotive domains respectively, further influencing supplier selection.
Customization Options and Emerging Trends
The demand for custom-tailored nuts and bolts and washers continues to rise, as industries seek highly specialized fasteners for unique applications. Manufacturers now accommodate orders for non-standard diameters, lengths, thread profiles, and even hybrid materials. Recent technological advancements include the incorporation of anti-backout features, self-locking threads, and coatings for electrical conductivity or biocompatibility. Laser etching enables traceability directly onto bolt heads, critical for aerospace and medical compliance tracking. Advanced manufacturing methods, such as cold heading and micro-machining, drive production tolerances down to ±0.005 mm. 3D printing in metal alloys also shows promise for creating prototype fasteners rapidly or fabricating designs previously deemed unmachinable. In tandem, manufacturers are deploying smart inspection systems using machine vision that catch micro-defects undetectable to the human eye, further reducing batch rejection and raising industry quality benchmarks.
Applications Across Precision Industries
The impact of tiny nuts and bolts and screws transcends traditional assembly roles, becoming foundational components in a range of high-tech industries. In the medical device sector, these fasteners are used to construct cardiac pacemakers, surgical tools, and endoscopic instruments—all requiring compact, sterile, and fail-proof designs. In electronics, the proliferation of wearable devices and miniaturized sensors has made reliable fastening mechanisms indispensable. The aerospace sector, meanwhile, utilizes titanium micro fasteners throughout unmanned aerial vehicles and satellite avionics, where every gram and cubic millimeter counts. Competing requirements for strength, lightweight construction, and vibration resistance drive ongoing innovation in this field. According to an industry survey by Fastener World in 2023, nearly 42% of design engineers now specify custom micro fasteners over off-the-shelf models, spurred by evolving functional demands and regulatory standards.
Case Studies: Innovations in Use
Real-world applications illustrate the indispensable role of tiny nuts and bolts. In 2022, a leading cardiovascular stent producer collaborated with a fastener specialist to develop a 1.2 mm low-profile locknut system, enabling assembly within confined surgical implants. This advancement reduced procedure times by 19% and postoperative complications by 7%. In the consumer electronics sector, a multinational smartwatch manufacturer switched to custom brass washer assemblies, combating galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals and extending product life by 24 months on average. Aerospace innovators have integrated self-locking titanium screws for CubeSat satellite modules, delivering weight savings of 18% alongside a 37% increase in joint resilience during vibration testing. These case studies demonstrate the ripple effect that the right micro fastener can have on safety, lifespan, and product performance across industries.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Tiny Nuts and Bolts in Future Technologies
The trajectory of engineering innovation rests upon seemingly inconspicuous elements, with tiny nuts and bolts at the forefront of the next wave of precision design. As products shrink and functionalities multiply, selecting optimized micro fasteners—and leveraging advances in materials, manufacturing, and quality management—will remain critical to market leadership. Through rigorous supplier selection, embracing customization, and applying the lessons of real-world cases, businesses can unlock higher reliability, improved safety, and extended product lifecycles. The ongoing evolution of micro fasteners assures their continued prominence within complex assemblies, solidifying their place as the linchpin of technical progress.

(tiny nuts and bolts)
FAQS on tiny nuts and bolts
Q: What are tiny nuts and bolts commonly used for?
A: Tiny nuts and bolts are commonly used in electronics, model building, and precision engineering. Their small size makes them ideal for securing miniature components. They provide reliable fastening where standard sizes are too large.Q: How do nuts and bolts and washers work together?
A: Washers are placed between the bolt head or nut and the surface to distribute pressure evenly. This helps prevent damage and loosening due to vibration. Using nuts, bolts, and washers together ensures a secure and lasting connection.Q: What is the difference between nuts and bolts and screws?
A: Bolts require a nut to fasten components, while screws are usually driven directly into materials. Nuts and bolts are ideal for removable joints. Screws are better for permanent or semi-permanent fastening.Q: Where can I buy tiny nuts and bolts for DIY projects?
A: You can buy tiny nuts and bolts at hardware stores, online retailers, and specialized hobby shops. Look for assortments based on size and material. Online platforms often offer bulk packages for convenience.Q: Are there different materials available for tiny nuts and bolts?
A: Yes, tiny nuts and bolts are made from materials like steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum. The material you choose depends on strength, corrosion resistance, and application. Stainless steel is popular for its durability and rust resistance.Latest News
-
High Quality SS Bolt Nut Washer - Durable Fastening Solutions for IndustriesNewsJul.08,2025
-
High Quality Slotted Hex Nut – Durable M12 Hex Nut & Slotted Bolt Compatible FastenerNewsJul.07,2025
-
Best Shuttering Shikanja Price & Construction Materials – High Quality, Durable & AffordableNewsJul.07,2025
-
5 8 Lock Washer – Heavy Duty, Rust Resistant, Ideal for Secure FasteningNewsJul.06,2025
-
Best 1 16 Toggle Bolt - Heavy Duty Anchors 3 Inch, 8 Inch Toggle Bolt & Wing Nut SolutionsNewsJul.06,2025