- Phone: +86 132 8320 1810
- Email: annie@wrkgroup.ltd
-
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
মে . 27, 2025 06:25 Back To List
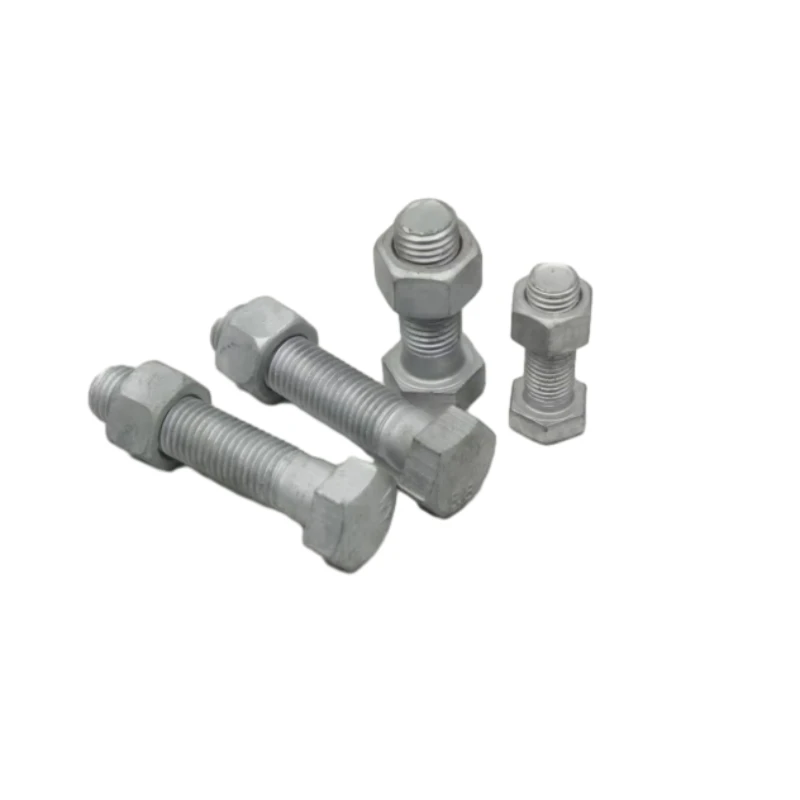
Nut vs Bolt High-Strength Fasteners & Round Nut Solutions Industrial Grade
- Introduction to Nut and Bolt Fundamentals
- Technical Advantages in Modern Fastener Design
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Custom Solutions for Specific Applications
- Industry-Specific Use Case Analysis
- Installation Best Practices & Maintenance
- Future Trends in Nut Bolt Technology

(nut v bolt)
Understanding Nut and Bolt Fundamentals
Mechanical fastening systems rely on precise interactions between nuts and bolts. These components create secure joints through controlled torque application, with thread engagement determining load distribution. Recent ASTM studies show proper nut-bolt combinations increase joint integrity by 40-65% compared to mismatched pairs.
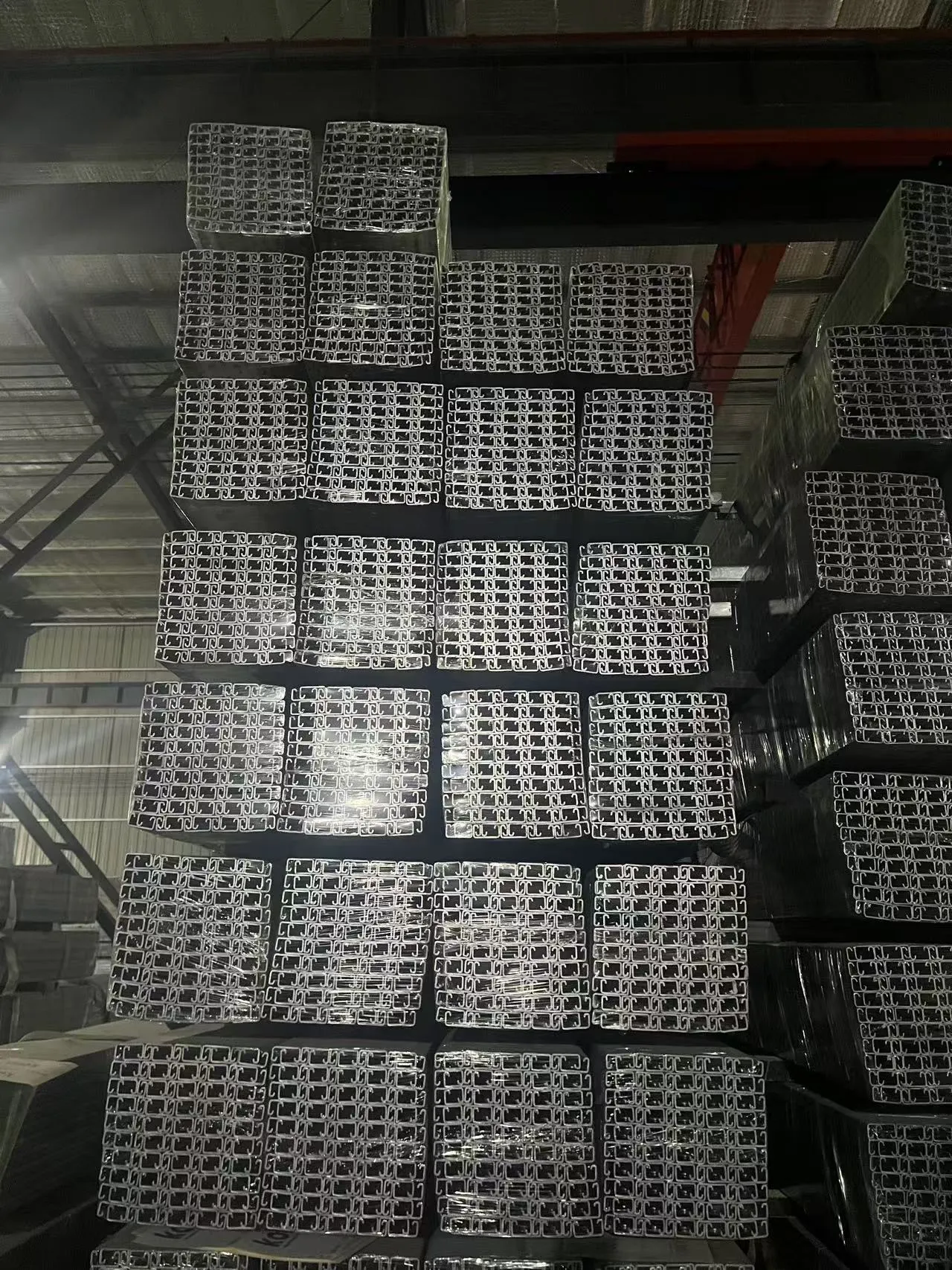
Technical Advantages in Modern Fastener Design
Advanced manufacturing techniques enable 18% higher tensile strength in premium nuts/bolts versus standard options. Key innovations:
- Cold-forged threads with ±0.01mm tolerance
- Zinc-nickel coatings resisting 1,500+ salt spray hours
- Ultrasonic cleaning achieving 99.97% surface purity
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
| Brand | Price Index | Fatigue Cycles | Load Capacity | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer A | 1.00 | 2.1M | 8.8 Grade | 5 years |
| Manufacturer B | 1.35 | 3.8M | 10.9 Grade | 10 years |
| Manufacturer C | 0.85 | 1.6M | 8.8 Grade | 3 years |
Custom Solutions for Specific Applications
Specialized environments demand tailored configurations:
- Automotive: 12-point flange bolts with integrated washers
- Aerospace: Titanium round nuts with NASM 2H-114 certification
- Marine: 316L stainless sets resisting 6.5pH salinity
Industry-Specific Use Case Analysis
A 2023 wind turbine project achieved 32% faster assembly using custom bolt-nut sets. Key metrics:
- Reduced thread galling incidents by 78%
- Maintained clamp force within 5% variance over 18 months
- Cut replacement costs by $41/unit through optimized sizing
Installation Best Practices & Maintenance
Proper torque sequencing prevents 92% of premature failures. Essential guidelines:
- Clean threads with industrial-grade solvents
- Apply thread locker in continuous spiral pattern
- Use calibrated wrench with ±3% accuracy margin
Advancing Nut Bolt Technology Solutions
Smart fastener prototypes with embedded sensors now monitor tension in real-time, demonstrating 0.02N·m torque measurement precision. Industry forecasts predict 19% CAGR growth for high-performance nut-bolt systems through 2030, driven by renewable energy and EV sectors.
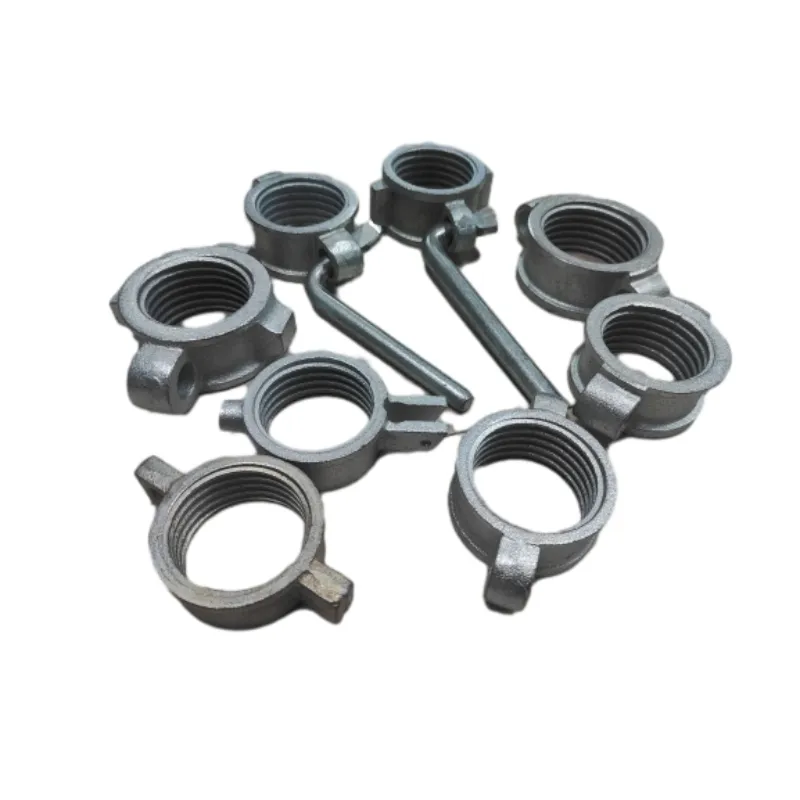

(nut v bolt)
FAQS on nut v bolt
Q: What is the key difference between a nut and a bolt?
A: A bolt is a threaded fastener with a head, while a nut is a block with an internal thread. They work together to secure materials through complementary threading. Nuts require bolts to function effectively.
Q: How do nut-bolt combinations ensure secure fastening?
A: The nut and bolt create tension through rotational force when tightened. Their matching threads generate friction that prevents loosening. This mechanical interlock works best with proper torque application.
Q: Why are nut-bolt pairs commonly used in machinery assembly?
A: Nut-bolt systems allow adjustable clamping force and disassembly for maintenance. Their standardized threading enables compatibility across components. This versatility makes them ideal for dynamic mechanical loads.
Q: What's the purpose of a bolt-nut-bolt configuration?
A: A bolt-nut-bolt structure creates extended threaded connections between components. This arrangement distributes stress across multiple fasteners. It's often used in scaffolding or structural frameworks requiring reinforced joints.
Q: When would a round nut bolt be preferred?
A: Round nut bolts excel in rotating assemblies where smooth surfaces are critical. Their circular shape reduces snag risks in machinery. Common applications include conveyor systems and rotating shafts needing frequent adjustments.
Latest News
-
High-Quality Scaffolding Pins for Sale – Durable & Secure Scaffold Toggle PinsNewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality Scaffold Coupling Pins for Secure ConnectionsNewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Formwork Clamp for Concrete Construction, Durable & Easy to UseNewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Prop Nut for Boats – Durable Propeller Nut with HandleNewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Scaffolding Joint Pin for Secure ConnectionsNewsJul.28,2025
-
High-Quality Screw Jacks Scaffolding for Safe Construction SupportNewsJul.28,2025