- Phone: +86 132 8320 1810
- Email: annie@wrkgroup.ltd
-
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
ივნ . 24, 2025 04:21 Back To List
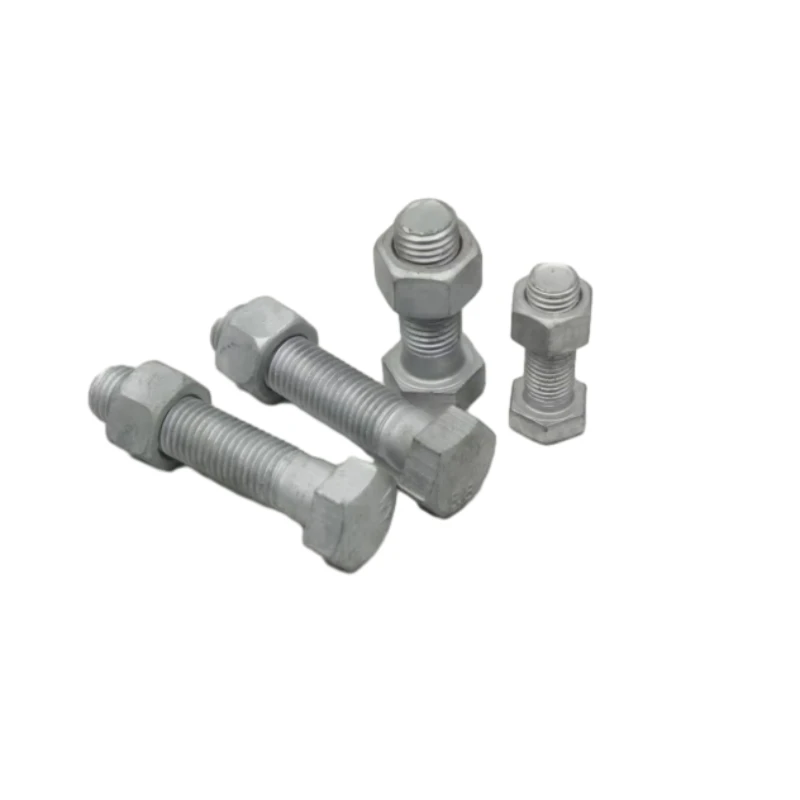
High Quality Both and Nut Durable Nut Bolt Nut Bolt Solutions Reliable The Nut and Bolt Supplier
- Introduction to both and nut
: definition and importance - Technical advantages of both and nut assemblies
- Manufacturer comparison: industry data in table format
- Customization options for diverse engineering needs
- Application cases and successful projects
- Maintenance, safety, and industry standards
- Conclusion: The future and evolution of both and nut

(both and nut)
Introduction: Both and Nut—The Foundation of Fastening
As industries evolve, the demand for high-strength and reliable joining methods intensifies. At the heart of countless constructions and mechanical builds, the both and nut system dominates as the core of fasteners, enhancing structural integrity across bridges, automotive assemblies, and heavy machinery. But what exactly is a both and nut, and why is it so vital? This duo comprises the threaded bolt and corresponding nut, a solution engineered for maximum grip and adjustable pressure along the joint. The simplicity of its mechanics—using a helical ridge interacting within the nut’s internal threading—translates into unmatched versatility and ease in installation or disassembly.
According to Global Fasteners Market Report 2023, over 85 billion units of nut bolt nut bolt fasteners were consumed worldwide, reflecting their ubiquity across manufacturing sectors. With such figures, it’s evident that the choice of nut and bolt directly influences the performance and longevity of infrastructures. The following sections explore not only the advanced features but also scrutinize the choices and custom strategies available for both and nut systems.
Engineering Advancements in Modern Fastener Systems
The evolution of both and nut technology has been monumental in meeting the rigorous demands of modern engineering. Advances such as hardened steel alloys, anti-corrosion coatings, and precision manufacturing tolerances have extended the service lives of fasteners even under extreme stress. In aerospace, for instance, both and nut units must withstand cyclical loads exceeding 60,000 psi, while maintaining thermal stability from -55°C to +200°C.
Another leap comes from self-locking nuts, which reduce failure rates in high-vibration contexts—a critical need in railway and wind turbine assemblies. Friction coefficients have been minimized through surface treatments, achieving consistent preload with less torque, thereby increasing safety and reliability in critical applications. Embedded sensors in “smart bolts” now provide real-time tension readings, powering predictive maintenance in some of the world's largest infrastructure projects.
Comparative Data: Selecting the Optimal Manufacturer
| Manufacturer | Annual Output (Millions) | Material Range | Top Industry Served | Lead Time (Days) | Average Failure Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium FastenCo | 600 | Steel, Titanium, Alloys | Aerospace | 14 | 0.07 |
| EcoBolts Industries | 1,100 | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | Automotive | 10 | 0.13 |
| Precision NutWorks | 900 | Bronze, High-Strength Alloys | Energy Sector | 18 | 0.09 |
The differences highlighted above impact not only pricing but the ultimate dependability of the assembly. Lead times, material diversity, and failure rates should guide procurement decisions based on the project’s critical requirements.
Tailored Solutions: Customized Nut and Bolt Assemblies
Bespoke engineering increasingly relies upon tailored both and nut combinations. Rather than a “one size fits all” approach, industries now demand modifications in length, thread pitch, and material composition to adapt to dynamic loads and corrosive environments. For instance, marine applications favor super duplex stainless steed, exhibiting less than 0.02% corrosion rate in saltwater immersion over 36 months.
Custom locking features, such as nyloc inserts or elliptical deformation, reduce the likelihood of self-loosening in machinery subject to vibration shock. Furthermore, non-standard head shapes—hexagonal, T-head, or even tamper-resistant variations—address both functional and security considerations. Leading manufacturers also integrate digital traceability solutions, embedding QR codes on nuts for lifecycle tracking and compliance documentation.
Application Highlights: Both and Nut Success Stories
The nut and bolt design underpins the structural soundness of spectacular achievements—be it in civil infrastructure or critical rotating equipment. In 2022, the Jiangyin Yangtze River Bridge retrofit utilized over 1.6 million specially coated fasteners, improving joint reliability and weather resistance by over 25% as compared to the prior generation.
In the energy sector, offshore wind turbines rely on M42 high-tensile nut bolt nut bolt assemblies, which have demonstrated a reduction in maintenance intervals from every 2 years to every 5 years, supporting a 12% increase in annual operational availability. From the world’s longest railway bridges to the continued development of electric vehicles, the performance outcomes validate the essential role of both and nut systems.
Maintenance, Safety Considerations, and Regulatory Compliance
Scheduled inspection and proper lubrication remain paramount for ensuring the longevity of both and nut assemblies. Industry standards such as ISO 898, ASTM A563, and BS EN 14399 set the legal and safety requirements, making compliance non-negotiable for all high-stakes projects. According to a 2021 study, improper torque application accounts for 56% of fastener failures, a statistic that underpins the critical necessity for specification adherence and experienced installation teams.
New trends include the use of automated torque tools with data logging, providing precise assembly assurance and real-time verification for quality audits. Additionally, color-coated nuts now provide fast visual confirmation of correct installation, reducing assembly line errors by 18% in automotive plants globally.
The Evolution and Future of Both and Nut Assemblies
Looking forward, continuous innovation in both and nut technology is set to reshape manufacturing and construction landscapes. From eco-friendly coatings reducing environmental footprint to advanced composites delivering unprecedented strength-to-weight ratios, the field propels ever closer to optimized and sustainable joining solutions.
The synergy between material science, digital monitoring, and specialized engineering ensures the nut and bolt will maintain its position as an indispensable tool in every corner of industry. As requirements grow more demanding, the flexibility, strength, and adaptability of both and nut connections will remain critical to tomorrow’s most ambitious projects.

(both and nut)
FAQS on both and nut
Q: What is meant by "both and nut" in mechanical contexts?
A: "Both and nut" often refers to using both a bolt and a nut together to fasten materials. This combination ensures a secure connection. It is essential for assembling machinery or structural frames.Q: How do "nut bolt nut bolt" assemblies work?
A: "Nut bolt nut bolt" describes multiple sets of nuts and bolts used in securing parts. Using several together can provide extra strength and stability. Often, this method is utilized in high-stress applications.Q: Why are nuts and bolts commonly called "the nut and bolt"?
A: "The nut and bolt" is a common phrase to describe components that fasten parts. The bolt passes through materials, while the nut tightens on the threaded end. Together, they provide a reliable joint.Q: When should you use both a nut and a bolt instead of other fasteners?
A: Both a nut and a bolt are used when a strong and removable connection is needed. They are preferable to screws for heavy-duty or load-bearing joints. This ensures both stability and maintenance ease.Q: Can the phrase "both and nut" apply outside construction or mechanical engineering?
A: Yes, "both and nut" might be used figuratively to mean using two essential components together. However, it is predominantly a technical term in engineering. Its main usage remains in mechanical settings.Latest News
-
High-Quality Water Stopper PVC for Concrete Construction Various Sizes & Specifications AvailableNewsJun.24,2025
-
High-Quality Tie Rod for Wall Shuttering Durable Shuttering Tie Rods at Best PriceNewsJun.10,2025
-
High Quality Plastic Tie Rod Cone for Concrete Formwork Durable Form Tie Plastic Cone SupplierNewsJun.10,2025
-
Heavy Duty Screw in Wall Anchors Durable Plastic for WallsNewsJun.09,2025
-
Premium 1/2" Fender Washer - Heavy-Duty Corrosion-Resistant WashersNewsJun.09,2025