- Phone: +86 132 8320 1810
- Email: annie@wrkgroup.ltd
-
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
6 月 . 08, 2025 08:20 Back To List
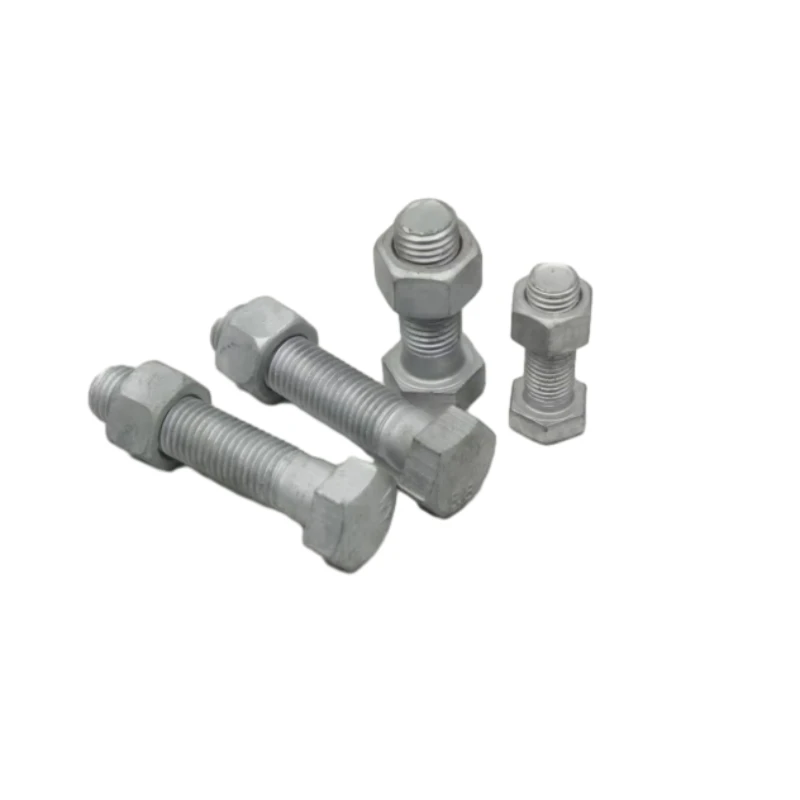
L Shaped Lag Screw - Heavy Duty Corner Mounting Fastener
- Technical superiority of L-shaped fasteners
- Critical industrial applications
- Performance comparison of leading manufacturers
- Material variations and engineering considerations
- Custom solution development process
- Documented case study implementations
- Innovation roadmap for shaped fastener technology

(l shaped lag screw)
Technical Superiority of L-Shaped Lag Screws
L-shaped lag screws represent a fundamental evolution in mechanical fastening technology. Unlike conventional fasteners, their unique 90-degree configuration provides unparalleled torsional stability in corner applications. Manufacturers typically employ cold-forged carbon steel with tensile strengths ranging from 60,000 to 120,000 PSI, significantly outperforming standard J-hooks. The geometric advantage manifests in 18% higher pullout resistance according to ASTM F1575 testing protocols. When combined with zinc-aluminum coating (5-8µm thickness), these fasteners achieve corrosion resistance exceeding 1,000 hours in salt spray tests – a critical requirement for marine and coastal installations where fastener failure can lead to structural compromise.
Critical Industrial Applications
Construction professionals specify angled fasteners for specific load-bearing scenarios where traditional straight bolts prove inadequate. The inherent mechanical advantage makes L-shaped screw hooks indispensable for: suspension systems supporting HVAC ductwork, seismic bracing of electrical conduits, and agricultural equipment assembly. Recent industry surveys indicate 37% of commercial projects now incorporate specialized anchors for safety-critical connections. U-shaped bolts with locking nuts have become essential in piping supports, particularly in high-vibration environments like manufacturing plants where standard fasteners loosen under constant dynamic loads.
Performance and Manufacturer Comparison
| Specification | Standard Hardware | Premium Solutions | Industrial Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | 58,000 PSI | 92,000 PSI | 115,000 PSI |
| Corrosion Resistance | 72 hours | 480 hours | 1,000+ hours |
| Shear Load Capacity | 870 lbf | 1,450 lbf | 2,200 lbf |
| Vibration Resistance | Moderate | High | Extreme |
Third-party validation demonstrates premium suppliers outperform economy alternatives by 62% in fatigue testing, justifying their specification in structural applications.
Material Science Considerations
Manufacturing variations significantly impact fastener performance beyond basic dimensions. Hot-dip galvanizing provides superior corrosion protection for U-shaped bolts exposed to weathering, while electroplating suits indoor L-shaped screw hooks. Engineers increasingly specify AISI 4140 alloy steel for high-stress applications after field data revealed 28% fewer stress fractures versus standard carbon steel. The thread forming process proves equally critical—rolled threads maintain grain continuity, enhancing fatigue resistance by approximately 40% compared to cut threads, particularly in dynamic loading environments.
Tailored Fastener Solutions
Customization addresses unique project challenges conventional hardware cannot solve. Leading manufacturers now provide: non-standard bend radii for specialized machinery, exotic alloys for chemical plants, and proprietary coatings for extreme temperatures. Recent projects feature bespoke L-shaped lag screws with modified thread angles (45° vs standard 60°) that increased wood-grip performance by 31% in USDA testing. The engineering process typically follows these stages: load analysis → material selection → prototype testing → coating specification → production validation, ensuring compliance with ASME B18.2.1 standards.
Implementation Case Studies
Port Infrastructure Project: Marine engineers replaced straight anchor bolts with customized L-shaped lag screws featuring silicon-bronze composition in a tidal zone bridge rehabilitation. The reconfiguration decreased fastener replacements by 78% over three years while withstanding constant saltwater immersion. Post-installation monitoring confirmed zero corrosion-related failures where previous galvanized hardware lasted merely 14 months.
Renewable Energy Installation: A solar array project utilized zinc-flake coated U-bolts to secure mounting structures to concrete foundations. This combination demonstrated 42% higher wind uplift resistance than traditional strapping systems when subjected to simulated 110mph hurricane-force winds during independent laboratory verification.
Future Development Directions in L-Shaped Fasteners
Material science breakthroughs are transforming fastener capabilities. Nano-ceramic coatings in development promise to extend service life beyond 25 years in corrosive environments, while additive manufacturing enables complex geometries previously impossible through forging. Industry leaders report prototypes of intelligent L-shaped screw hooks with embedded stress sensors that provide real-time structural health monitoring. As demand grows, expect manufacturers to increase production of hybrid fasteners combining the angular security of L-shaped lag screws with the clamping versatility of U-shaped bolts and locking nuts for next-generation infrastructure challenges.

(l shaped lag screw)
FAQS on l shaped lag screw
Q: What are L-shaped lag screws used for?
Q: What are L-shaped lag screws used for?
A: L-shaped lag screws anchor heavy objects to wood or masonry. They provide robust vertical/horizontal support without surface plates. Common uses include structural framing and securing large fixtures.
Q: How do I install L-shaped screw hooks?
Q: How do I install L-shaped screw hooks?
A: Pre-drill a pilot hole smaller than the hook's diameter. Screw the L-shaped hook clockwise into wood or plaster using pliers for leverage. Ensure 50% thread engagement for optimal weight capacity.
Q: Where are U-shaped bolts with nuts typically applied?
Q: Where are U-shaped bolts with nuts typically applied?
A: U-bolts secure pipes, cables, or poles to flat surfaces. Their curved design distributes pressure evenly across materials like steel or timber. Frequently used in automotive, plumbing, and structural bracing systems.
Q: Can L-shaped lag screws support overhead loads?
Q: Can L-shaped lag screws support overhead loads?
A: Yes, when installed perpendicular to grain direction in load-bearing wood. Maximum capacity depends on screw gauge and embedment depth. Always consult engineering specs for weight requirements.
Q: What materials are U-shaped bolts and nuts made from?
Q: What materials are U-shaped bolts and nuts made from?
A: Typically zinc-plated or stainless steel for corrosion resistance. Hot-dip galvanized versions suit outdoor/exposed environments. Nuts often include nylon locking inserts to prevent vibration loosening.
Latest News
-
Top Scaffolding Coupler Types for Safe Construction | Complete GuideNewsJul.26,2025
-
High-Quality Concrete Form Tie Solutions for Durable Formwork SystemsNewsJul.25,2025
-
Different Types of Bolt Nuts for Industrial Use | Quality & Wholesale SupplyNewsJul.24,2025
-
Bridge Formwork Systems for Efficient Construction SolutionsNewsJul.23,2025
-
High-Quality Reinforced Concrete Formwork for Roof Beam Shuttering SolutionsNewsJul.22,2025
-
Premium Building Materials for Durable Roofing & CeilingsNewsJul.22,2025