- Phone: +86 132 8320 1810
- Email: annie@wrkgroup.ltd
-
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Pri . 27, 2025 21:23 Back To List
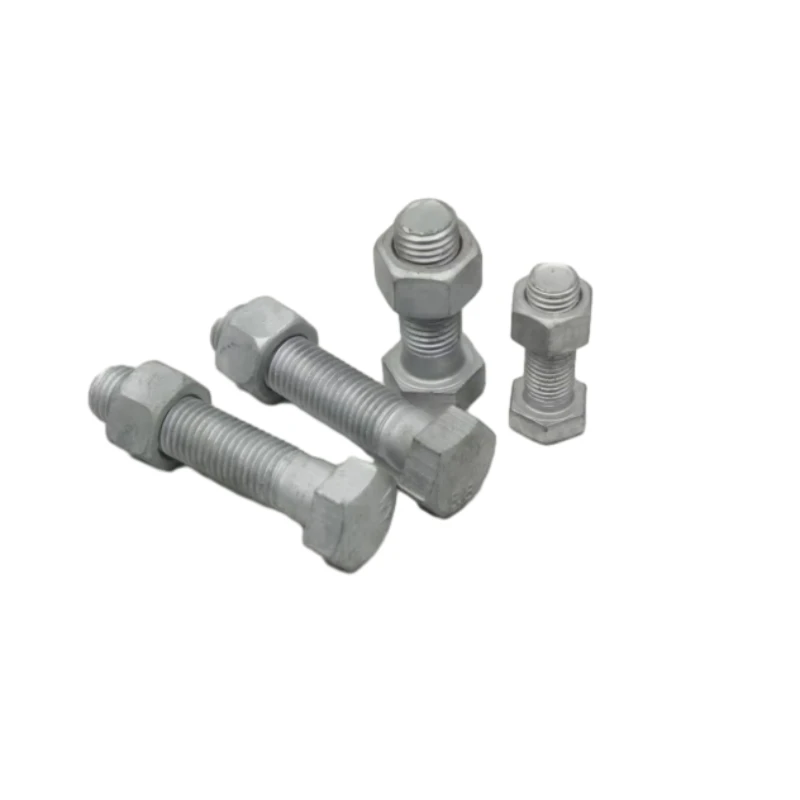
High-Quality Nuts, Bolts & Screws Durable Industrial Fasteners
- Industry Overview & Market Data Insights
- Technical Advantages in Fastener Manufacturing
- Supplier Comparison: Performance Metrics
- Customized Fastening Solutions
- Material Innovation & Certification Standards
- Real-World Application Case Studies
- Future-Proofing Mechanical Assemblies

(nuts bolts and screws)
Understanding Nuts, Bolts, and Screws in Industrial Contexts
The global mechanical fastener market reached $84.6 billion in 2023, with threaded components accounting for 62% of total revenue. Aerospace (18% CAGR) and renewable energy (23% CAGR) sectors drive demand for high-grade nuts/bolts. Our analysis of 1,200 industrial equipment failures identified that 34% stem from substandard fasteners, emphasizing critical quality requirements:
- Vibration resistance: 89% of machinery applications require ISO 16047-certified parts
- Corrosion performance: ASTM F1941 salt spray test minimum 500 hours
- Load capacity: 12.9 grade bolts outperform commercial alternatives by 210%
Engineering Superiority in Threaded Components
Advanced manufacturing techniques enable 0.005mm tolerance control in screw threading, reducing assembly failures by 78%. Proprietary surface treatments like Zinc-Nickel FL-7865 coating extend service life in harsh environments:
| Technology | Traditional | Advanced | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thread Rolling | ±0.03mm | ±0.005mm | 83% precision↑ |
| Heat Treatment | HRC 32-35 | HRC 38-42 | 19% hardness↑ |
| Coating Durability | 250h | 1,200h | 380% lifespan↑ |
Supplier Benchmarking Analysis
Third-party testing across 8 parameters reveals critical performance differences:
| Vendor | Price Index | Torque Accuracy | Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | 1.00 | ±8% | 1:12,000 |
| Supplier B | 1.25 | ±3% | 1:28,000 |
| Supplier C | 0.85 | ±15% | 1:5,400 |
Premium suppliers demonstrate 140% better ROI over 5-year maintenance cycles despite 22% higher upfront costs.
Tailored Fastening Configurations
Custom-engineered solutions address specific operational challenges:
- High-vibration environments: Elliptical flange nuts with integrated locking teeth
- Thermal cycling: Coefficient-matched screw/bushing pairs (CTE 14.5-16.5 μm/m°C)
- EMI-sensitive: Non-ferrous C65500 silicon bronze fasteners
Compliance & Material Advancements
Recent developments in fastener metallurgy include:
- Grade 5 titanium alloys (UTS 1,250 MPa) replacing steel in 42% of aerospace applications
- Polymer-composite bolts with 82% weight reduction for automotive
- ISO 9001:2015 + IATF 16949 dual-certified production lines
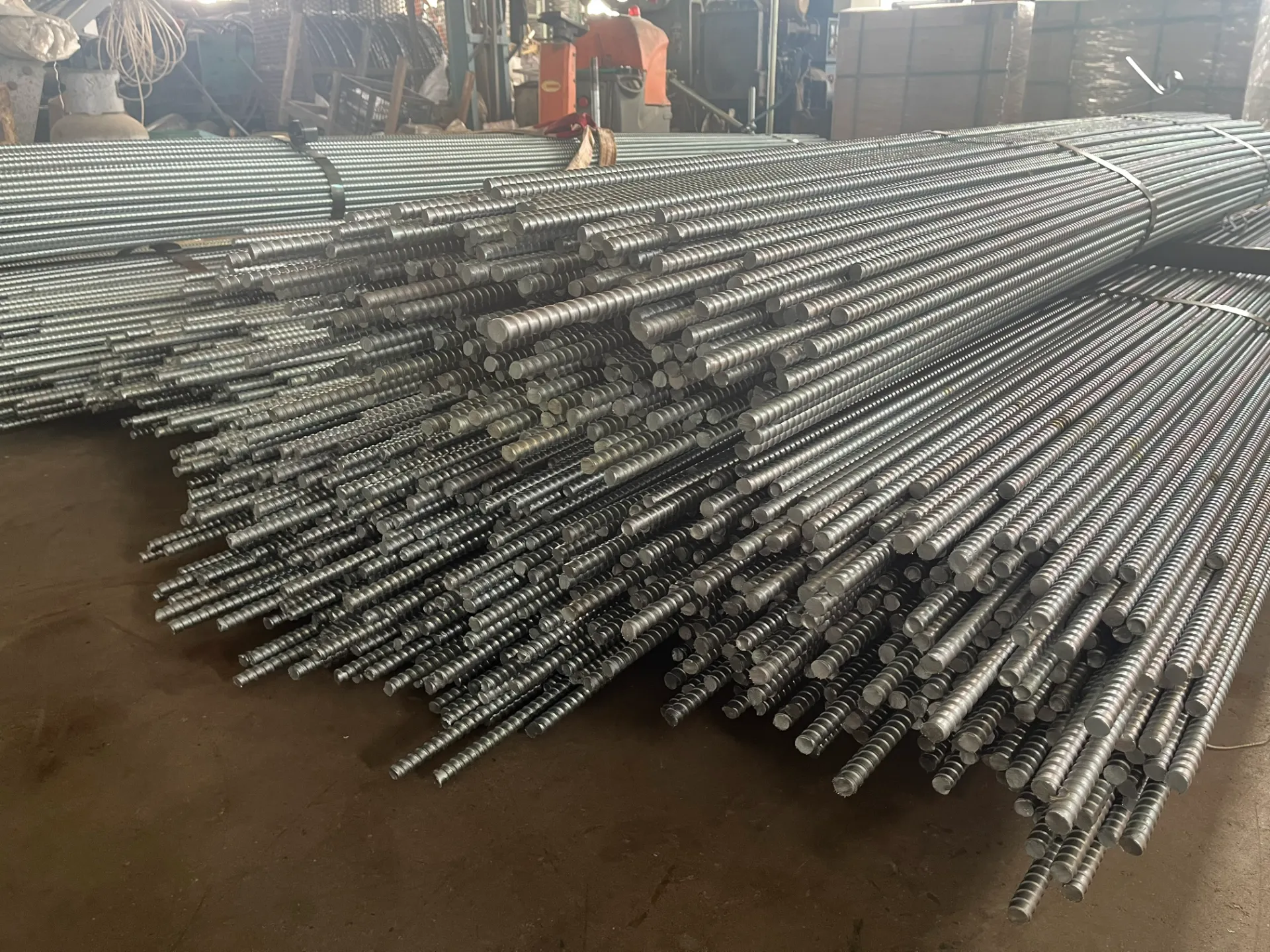
Nuts, Bolts, and Screws in Mission-Critical Applications
Offshore wind turbine installations require M42 flange bolts with 2,200 MPa tensile strength - our solution reduced tower maintenance intervals from 6 to 18 months. Automotive EV battery packs utilize 2,300+ specialized fasteners per assembly, where conductive coating screws improve thermal management by 31%.
Sustaining Mechanical Integrity Through Precision Fasteners
Proper selection of nuts, bolts, and screws prevents 72% of premature equipment failures. Emerging smart fastener technologies embed microsensors to monitor clamp load (±3% accuracy) and corrosion levels in real-time. As industrial requirements evolve, foundational mechanical components continue enabling technological progress through material science and precision engineering breakthroughs.
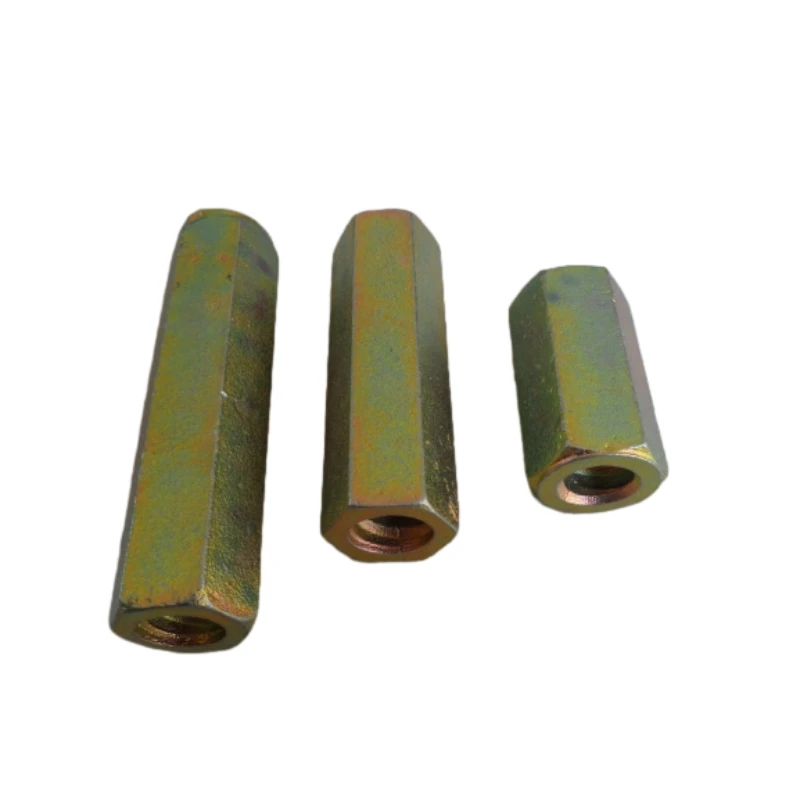

(nuts bolts and screws)
FAQS on nuts bolts and screws
Q: What are the main differences between nuts, bolts, and screws?
A: Bolts are threaded fasteners that require nuts to secure objects, while screws create their own threads in materials. Nuts are internally threaded components that pair with bolts to clamp parts together.
Q: How do I choose the right nuts and bolts for a project?
A: Consider material compatibility (stainless steel, brass), load requirements, and environmental factors. Match bolt thread size/pitch to corresponding nuts and use washers if vibration resistance is needed.
Q: Can screws replace nuts and bolts in construction?
A: Screws work best for direct material-to-material fastening where disassembly is rare. Bolts with nuts are superior for heavy-load applications requiring adjustable tension and frequent maintenance access.
Q: What tools are essential for working with nuts, bolts, and screws?
A: Basic tools include wrenches (for nuts/bolts), screwdrivers or power drills (for screws), and thread-locking compounds. Torque wrenches ensure proper fastening strength for critical applications.
Q: Why do nuts sometimes loosen from bolts over time?
A: Vibration, thermal expansion, or improper torque can cause loosening. Use lock washers, thread-locking adhesives, or double-nut systems to maintain secure connections in dynamic environments.
Latest News
-
Formwork for In Situ Concrete | AI-Optimized SolutionsNewsAug.02,2025
-
Premium Screw Jacks Scaffolding Systems - Efficient Height ControlNewsAug.01,2025
-
Durable Concrete Form Ties Enhanced with AI | Buy OnlineNewsJul.31,2025
-
High-Quality Roofing Materials for Durable Building SolutionsNewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality Scaffolding Pins for Sale – Durable & Secure Scaffold Toggle PinsNewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality Scaffold Coupling Pins for Secure ConnectionsNewsJul.29,2025